Introduction to Cemented Carbides
Cemented carbides with "hard" and "heavy" characteristics
Cemented carbides are alloy crafted by sintering hard metal carbide powders. It boasts hardness second only to diamond and is approximately twice the weight of iron.


Typically, it denotes a blend of tungsten carbide (WC) and cobalt (Co) as the binder, fused through sintering. It finds primary application in fields like cutting tools or molds, where exceptional wear resistance is indispensable.
Cemented carbide contributes to enhanced machining precision and reduced manufacturing costs
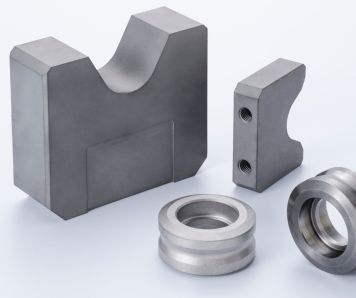
Cemented carbides are primarily used in fields where wear resistance, such as cutting processes and mols, is required. Depending on the application, materials such as titanium carbide (TiC) or tantalum carbide (TaC) may be added to enhance material properties. Cemented carbides exhibit minimal hardness reduction at high temperatures and are highly resistant to wear, making them suitable for use as a material for metalworking cutting tools (such as lathe and milling tools) and in the manufacturing of automotive parts (engine components, transmission parts. steering components, etc.). Its use significantly contributes to improving the precision of individual parts and reducing manufacturing costs.